How to Regulate Meal Timing and Portion Sizes for Diabetics
Regulating meal timing and portion sizes is crucial for diabetics to maintain stable blood glucose levels, avoid spikes and dips in blood sugar, and support overall health.
Here are comprehensive guidelines to help diabetics manage their meal timings and portion sizes effectively:
Eat Regularly:
Consistent Meal Schedule:Aim to eat at the same times each day. This helps your body regulate blood sugar levels more effectively.
Plan for three main meals and two to three snacks distributed evenly throughout the day.
Avoid Skipping Meals: Skipping meals can lead to a drop in blood sugar levels followed by overeating, which can cause spikes in glucose levels.
Always carry a healthy snack in case you are unable to sit down for a regular meal.
Monitor Portion Sizes and Choose Balanced Meals:
Follow Portion Guidelines: Use measuring cups, spoons, or a food scale to accurately portion your food, especially when starting a new eating plan.
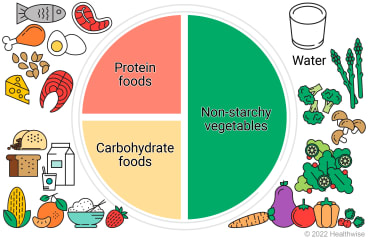
Visual aids like the Plate Method can help: half the plate should be vegetables, a quarter lean protein, and a quarter whole grains or starches.
Read Nutrition Labels: Pay attention to serving sizes listed on food labels to ensure you are consuming the recommended portion, which can help keep your blood sugar levels in check.
Choose Balanced Meals:
Include Macronutrients: Each meal should include a balance of carbohydrates, protein, and fats.
Carbohydrates have the most direct impact on blood sugar, so pair them with protein and healthy fats to slow their absorption.
Incorporate Fiber: Foods high in fiber help slow the absorption of sugar, aiding in maintaining stable blood glucose levels.
Include plenty of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and legumes.
Control Carbohydrate Intake and Snack Wisely:
Carbohydrate Counting: Count the grams of carbohydrates in your meals to ensure you’re not consuming too many or too few carbs.
Adjust your insulin or medication accordingly as guided by your healthcare provider.
Use Glycemic Index (GI): Opt for low to medium GI foods, which have a slower impact on blood sugar levels compared to high GI foods.
Examples include whole oats, quinoa, and legumes.
Snack Wisely:
Healthy Snacks: Choose snacks that provide sustained energy and include a combination of carbohydrates, protein, and fats.
Examples include a small apple with almond butter or Greek yogurt with berries.
Portion Control: Be mindful of the portion sizes of your snacks. Overeating even healthy snacks can lead to blood sugar spikes.
Adjust for Physical Activity and Stay Hydrated:
Pre- and Post-Exercise Nutrition: Eat a small snack with carbohydrates and protein before physical activity to prevent low blood sugar.
Post-exercise, replenish your energy levels with a balanced meal.
Monitor and Adjust: Check your blood sugar levels before and after exercise and adjust your food intake accordingly.
Stay Hydrated:
Drink Water: Staying hydrated is important for overall health and can help control blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water a day.
Avoid sugary drinks which can cause rapid spikes in blood glucose.
Incorporating these guidelines into your daily routine can help manage diabetes more effectively and contribute to overall health and well-being.
Remember to consult with your healthcare provider or a dietitian to tailor these recommendations to your specific health needs and conditions