How to Monitor and Adjust in Diabetes
Effective management of diabetes requires continuous monitoring and adjustment of various aspects of your health regimen.
Here’s a comprehensive guideline to help you monitor and adjust your diabetes management:
Regular Blood Glucose Monitoring:
Self-Testing: Use a blood glucose meter to test your blood sugar levels multiple times a day.
This helps you understand how different foods, activities, and medications affect your blood sugar.
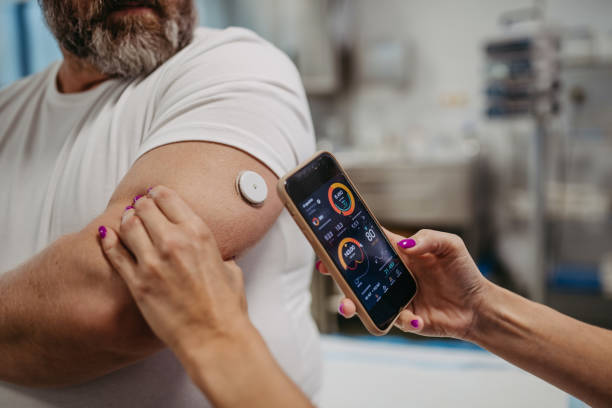
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): Consider using a CGM device, which provides real-time data on blood glucose levels throughout the day and night.
This continuous feedback can be invaluable for making immediate adjustments.
Target Ranges: Work with your healthcare provider to establish your target blood glucose ranges before meals, after meals, and at bedtime.
Maintain a Diabetes Journal and Hemoglobin A1c Testing:
Record Keeping: Keep a detailed record of your blood glucose levels, insulin doses, meals, physical activity, and any symptoms you experience.
This can help identify patterns and triggers.
Review and Adjust: Regularly review your journal with your healthcare provider to make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
Hemoglobin A1c Testing:
Periodic Checks: Have your A1c levels checked at least twice a year. This test provides an average of your blood glucose levels over the past 2 to 3 months.
Understand Your Results: A lower A1c level indicates better blood sugar control.
Discuss the results with your healthcare provider to evaluate the effectiveness of your current management plan.
Adjusting Medications, Diet and Exercise Modifications:
Medication Review: Regularly review your medications with your healthcare provider, especially if you notice any changes in your blood glucose patterns.
Insulin Adjustment: If you use insulin, learn how to adjust your doses based on your blood sugar readings, carbohydrate intake, and physical activity.
This is particularly crucial for those on intensive insulin regimens.
Diet and Exercise Modifications:
Carbohydrate Counting: Count your carbohydrate intake to better manage how it impacts your blood sugar levels. Learn to adjust your insulin or medications accordingly.
Physical Activity: Regular exercise can significantly impact blood sugar levels.
Note how different types and durations of exercise affect your readings and adjust your physical activity accordingly.
Stress Management, Hydration and Sleep:
Identify Stressors: Recognize sources of stress and their impact on your blood sugar levels.
Common stressors include work, relationships, and major life changes.
Stress-Reduction Techniques: Incorporate stress-management techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, and hobbies to help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Hydration and Sleep:
Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration helps manage blood sugar levels. Aim for consistent fluid intake throughout the day.
Prioritize Sleep: Ensure you get enough restful sleep each night. Poor sleep can adversely affect blood sugar control.
Frequent Consultations:
Regular Check-Ups: Schedule regular appointments with your healthcare provider to review your overall diabetes management plan and make any necessary adjustments.
Specialist Referrals: If needed, seek advice from specialists such as endocrinologists, dietitians, or diabetes educators for more personalized and detailed care.
By following these guidelines, you can effectively monitor and adjust your diabetes management plan to maintain optimal blood sugar control and overall health.
Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice tailored to your individual needs.