The Role of Exercise in Diabetes Control
Exercise is a vital component of diabetes management, offering numerous benefits that contribute to improved blood sugar control and overall health.
Regular physical activity can enhance insulin sensitivity, reduce body fat, improve cardiovascular health, and boost mental well-being.
This comprehensive article outlines guidelines on how to effectively incorporate exercise into a diabetes management plan.
Understanding the Benefits of Exercise for Diabetics
Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Engaging in regular physical activity helps muscle cells become more responsive to insulin, allowing for more efficient glucose uptake and lowering blood sugar levels.
Weight Management: Exercise aids in burning calories and achieving or maintaining a healthy weight, which is crucial for managing diabetes effectively.
Cardiovascular Health: Many individuals with diabetes are at an increased risk of heart disease. Regular exercise strengthens the heart and improves circulation, helping to mitigate these risks.
Enhanced Mood and Mental Health: Physical activity can reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety, promoting overall emotional well-being and providing a sense of accomplishment.
Guidelines for Incorporating Exercise into a Diabetes Management Plan
1. Assess Individual Fitness Levels
Consult with Healthcare Providers: Before starting any exercise regimen, individuals should consult their healthcare team to create a safe and effective workout plan tailored to their health status and fitness levels.
Personal Health Considerations: Take into account any complications or limitations, such as joint issues or cardiovascular conditions, when selecting types of exercise.
2. Set Realistic Exercise Goals
Short-term and Long-term Objectives: Establish achievable goals, such as exercising for 30 minutes a day, five times a week, or integrating strength training into the routine a couple of times a week.
Monitor Progress: Utilize fitness trackers, mobile apps, or journals to keep track of activities, durations, and improvements in fitness over time.
3. Choose Appropriate Types of Exercise
Aerobic Activities: Engage in moderate-intensity aerobic exercises, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, to boost cardiovascular health and improve insulin sensitivity.
Strength Training: Incorporate resistance training at least two days a week. This can involve using free weights, resistance bands, or bodyweight exercises to build muscle mass, which aids in glucose metabolism.
Flexibility and Balance: Include stretching and balance exercises to enhance physical stability and prevent injuries. Activities like yoga or tai chi can be beneficial.
4. Develop a Consistent Routine
Make Exercise a Habit: Schedule workouts at consistent times to establish a routine.
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly, as advised by health guidelines.
Mix It Up: Vary the types of exercises to keep the routine engaging and reduce the risk of injury.
5. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
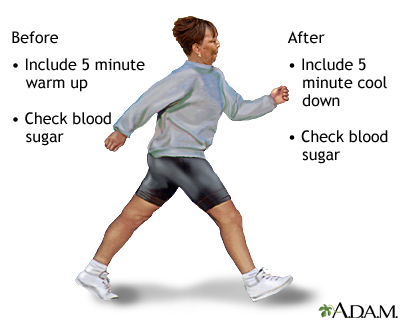
Check Before and After Exercise: Monitor blood glucose levels before, during (if exercising for an extended period), and after workouts to understand how exercise affects individual blood sugar responses.
Know When to Eat: Adjust meal timing and carbohydrate intake, if necessary, based on activity levels, especially for longer or more intense workouts.
6. Stay Hydrated
Drink Water: Hydration is crucial, especially during physical activity. Ensure adequate fluid intake to prevent dehydration, particularly if exercising in hot conditions.
7. Collaborate with Professionals
Work with a Fitness or Diabetes Coach: For additional support, consider working with fitness trainers knowledgeable about diabetes management. They can provide tailored exercise plans and help monitor progress.
Conclusion
Incorporating exercise into diabetes management is not just a suggestion but a fundamental part of achieving better health outcomes.
By understanding the benefits, setting realistic goals, selecting appropriate activities, and maintaining consistency, individuals with diabetes can significantly enhance their quality of life and overall health.
As with any lifestyle change, it’s essential to regularly review and adjust exercise plans in consultation with healthcare professionals to ensure they remain effective and safe.